Fast, High-Precision SLS 3D Printing Services
- Real-Time Production Updates
- Parts as Fast as Few Days
- Rapid Turnaround for Complex Parts
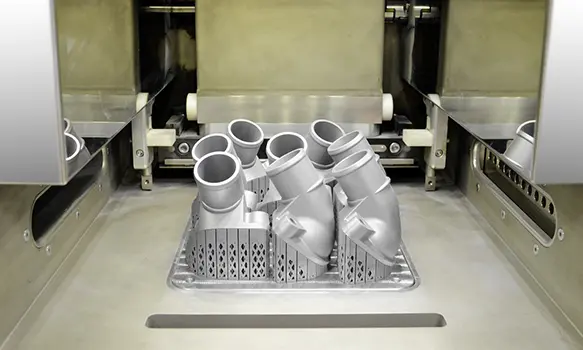
What is SLS 3D Printing?
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is an advanced 3D printing technology that creates highly accurate and durable parts for end-use applications, low-volume production, and rapid prototyping. As one of the most cost-effective industrial 3D printing methods, the SLS process can produce parts in bulk and often requires fewer support structures, minimizing material waste and production time.
The SLS process utilizes a high-power CO2 laser to fuse fine plastic powder particles into precise three-dimensional shapes. It scans cross-sections from 3D digital models, like CAD files, onto a powder bed, selectively fusing the material layer by layer. This continues until the part is fully formed, resulting in complex geometries with excellent mechanical properties.
The capability of SLS to produce functional prototypes and end-use parts with minimal post-processing makes it essential for industries such as aerospace, automotive, consumer products, and medical devices.
Why Choose NPI SLS 3D Printing Service
- No minimum order quantity
- Metal or plastic 3D printed prototype and production parts in 3-10 days
- Precision custom 3D printing parts at affordable prices
- Online free quote in the shortest time
- Single prototypes or complex shapes are both allowed
- A wide selection of metal or plastic materials
- Commercial and industrial-grade 3D printers
- Cooperative supplier assistance project
- Provide a quick solution for small batches of complex prototypes
- 3D printing services for metals and plastics
- Meet the rapid needs of complex prototype designers
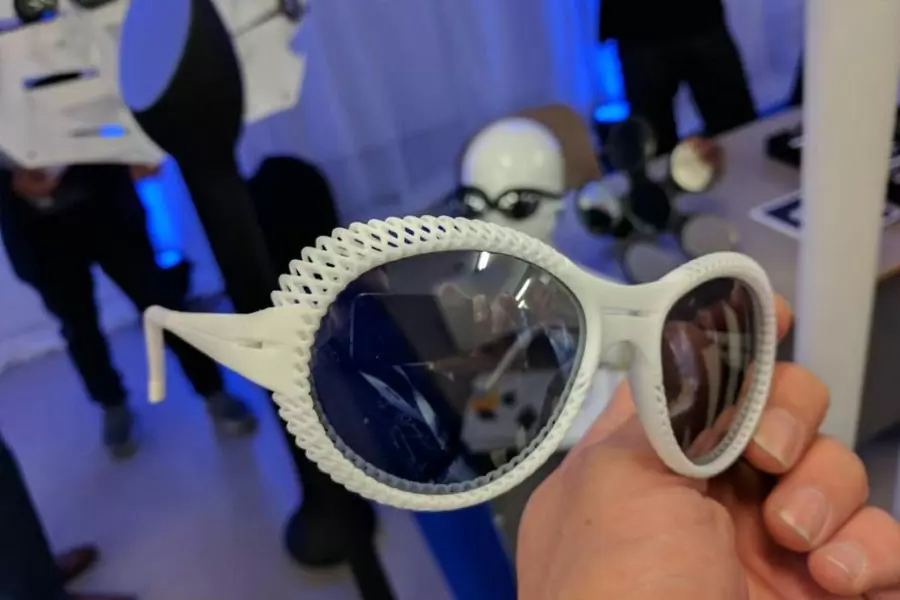


SLS Design Guide
How does SLS 3D printing work?
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is an advanced 3D printing method. It uses a laser to melt powdered materials into solid shapes.Here’ s how it works:
- Powder Layering: The process starts with a thin layer of powder. This powder is usually plastic, metal, or ceramic. It is spread evenly across the build platform.
- Laser Activation: A strong laser scans the design’s cross-section using a 3D computer model. It heats and fuses the powder particles together.
- Layer-by-Layer Construction: After the laser finishes one layer, the build platform lowers a bit. Then, a new layer of powder is added. The laser then fuses the next layer, and this process repeats until the entire object is complete.
- Cooling and Removal: Once the printing is finished, the build chamber is allowed to cool down. The unfused powder supports the object, making it easy to handle without additional support structures.
- Post-Processing: The final step involves removing any excess powder and performing any necessary post-processing, such as cleaning, surface finishing, or additional treatment to enhance properties.
SLS technology is particularly valued for its ability to produce complex geometries and functional prototypes, making it a popular choice in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and healthcare etc.
